Oil, gas, and renewables are all growing.
|
Listen To This Story
|
US energy production is going gangbusters.
Despite persistent false claims that the Biden administration is waging an “unprecedented assault” on American energy, the US is producing energy at a pace never seen before and from a broad mix of sources and locations throughout the country. In fact, the data illustrates that we’re experiencing an unprecedented renaissance of American energy production and innovation.
The chart below is interactive — hover over the lines to see the details.
The US Is Producing More Energy than Ever Before
This graph shows primary energy production, in other words, extraction of fossil fuels and generation of electricity by renewables and nuclear.
This graph shows primary energy production data from the Energy Information Administration. For fossil fuels, “primary energy production” is the energy content in the coal, oil, or gas that’s extracted. For nuclear and renewables, it’s the amount of electricity generated. Note that this is not the same as energy consumed; it’s simply the energy produced.
The production of oil, methane gas (commonly called “natural” gas), and renewables is growing. Nuclear power is holding fairly steady, and the only source of energy that has declined significantly is coal.
The largest sources of energy production in the US are oil and gas. Extraction of these fuels began to surge around 2007 when the development of hydraulic fracturing, or fracking, gave rise to the shale oil boom. Oil and gas production continues to set records, even while US consumption of oil is declining and methane gas consumption is not increasing at anywhere near the rate of production. The end result is that the US is exporting more of these fuels than ever.
Renewables Count for More than They Appear.
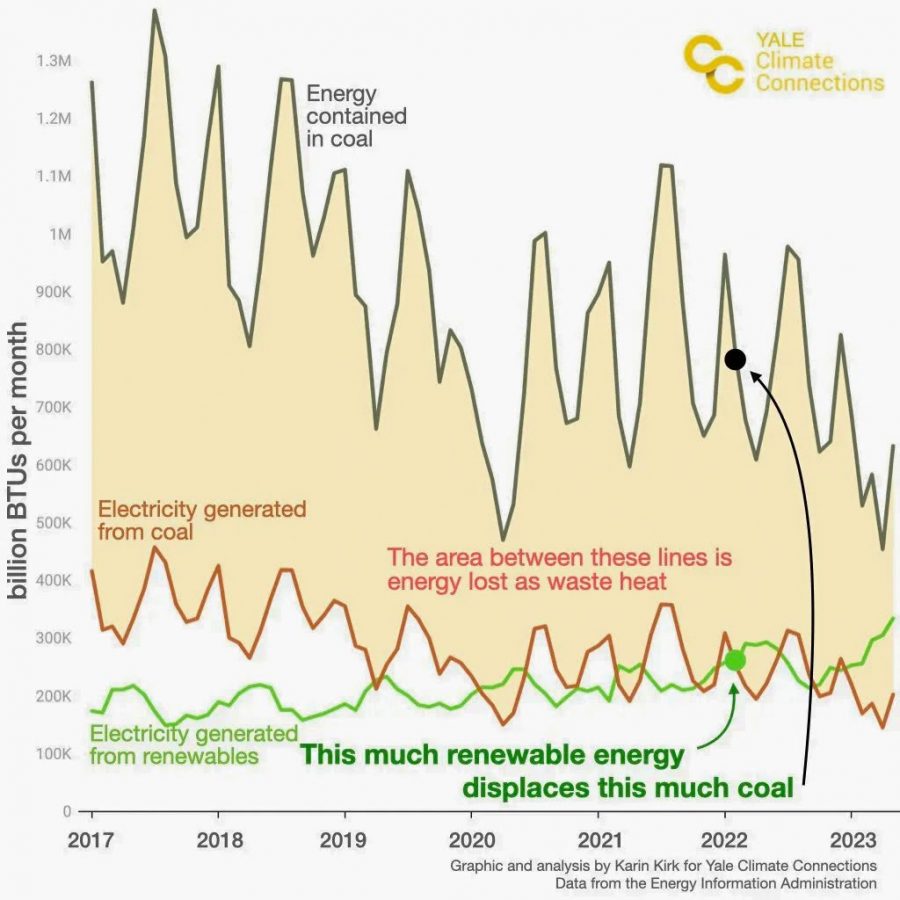
Renewables may look small on the graph above, but the more accurate interpretation is that fossil fuels appear much larger than the useful energy they provide. Burning fossil fuels in power plants or internal combustion engines is highly inefficient. The majority of energy in every barrel of oil and railcar of coal ends up as wasted heat.
Renewables don’t need to transform heat into electricity, so they avoid the energy losses that are inherent in burning fuels to create electricity. The upshot is that every unit of wind, hydro, or solar will replace double or triple that amount of fossil fuels.
Energy savings are an added benefit of switching to renewables, as is illustrated in the chart below. For more details, see the accompanying story, “The little-known, massive advantage that renewables hold over coal.”
This story by Karin Kirk was originally published by Yale Climate Connections and is part of Covering Climate Now, a global journalism collaboration strengthening coverage of the climate story.





